R for modellers - Vignette 09
Data wrangling
Julien Arino


Department of Mathematics
University of Manitoba*
Vignette 09
Data wrangling
Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba*
Canadian Centre for Disease Modelling
- The University of Manitoba campuses are located on original lands of Anishinaabeg, Cree, Oji-Cree, Dakota and Dene peoples, and on the homeland of the Métis Nation.
Outline
Data wrangling
Data wrangling
Data you acquire is rarely in a format that is immediately useful for your purposes
Data wrangling is the process of transforming and mapping data from one “raw” data form into another format to make it more appropriate and valuable for a variety of downstream purposes
Data wrangling methods: “old school” vs dplyr vs sqldf
Can go “old school”
dplyr is part of the tidyverse set of libraries. Loads magrittr and its pipe %>%
sqldf allows to use SQL on dataframes.. interesting alternative if you know SQL
3 ways to keep only the data for one country
Let us load some data for SARS-CoV-1 (2003) that I collected some time back
github_URL = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/"
repo_URL = "julien-arino/datasets/master/"
file_name = "SARS_data.csv"
SARS_URL = paste0(github_URL, repo_URL, file_name)
SARS = read.csv(SARS_URL)We want to keep the data for one country (e.g., Canada)
Old school: SARS$country == ctry
SARS$country == ctry is a vector of TRUE (entries in SARS$country which do equal ctry) and FALSE (entries in SARS$country which do not equal ctry)
Using this vector as an index for SARS keeps only the entries for which the index is TRUE
Old school 2: which(SARS$country == ctry)
Same as before, except that here which returns the indices of the entries for which SARS$country == ctry is TRUE, so idx takes the form
These are the indices in the original dataframe SARS of the entries we want to keep
Benefits of gathering indices using which
We can make different index sets corresponding to different criteria, then combine them using intersect, union and setdiff
For instance, if we want to keep only the entries for which the country is Canada and the date is before 2003-04-30
idx_CAN = which(SARS$country == ctry)
idx_date = which(SARS$toDate < "2003-04-30")
idx_CAN_date = intersect(idx_CAN, idx_date)Using sqldf
library(sqldf)
query = paste0("SELECT * ",
"FROM SARS ",
"WHERE country = '",
ctry, "'")
SARS_selected = sqldf(query)Using dplyr
Create incidence for the selected country. diff does difference one by one, so one less entry than the vector on which it is being used, thus we pad with a 0
Keep only positive incidences (discard 0 or negative adjustments)
SARS_selected = SARS_selected %>%
filter(incidence > 0)Plot the result. Before plotting, we need to make the dates column we will use be actual dates..
Select the data columns needed
We use a function from incidence2 to format the data as needed for the plot
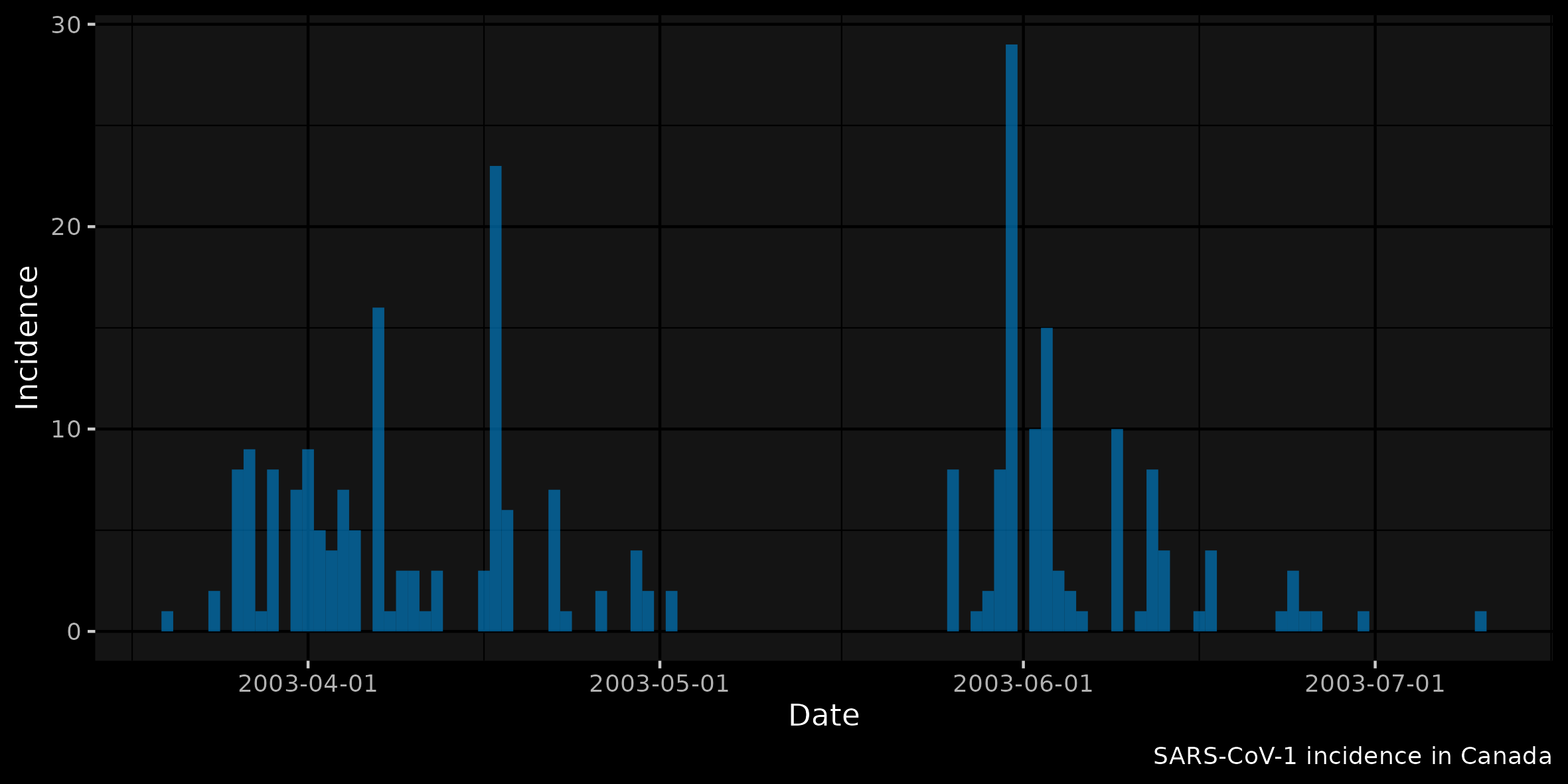
Finally, we plot using ggplot2
library(ggplot2)
plot(incid) +
labs(fill = "Type") +
xlab("Date") + ylab("Incidence") +
labs(caption =
sprintf("SARS-CoV-1 incidence in %s", ctry)) +
theme(legend.position = "none")(Note that the following plot uses + ggdark::dark_mode())
bg contain